
The 5th generation global wireless standard, 5G, is all the rage this year. Following 1G, 2G, 3G, and 4G, it is a network that has been designed to connect devices, objects, and machines with never-before-seen precision. It is supposed to deliver the highest multi-Gbps peak data speed with a minimal lag. Multiple companies within the mobile realm have been working on adapting to this new network such as Samsung, Google, Xiaomi, etc.

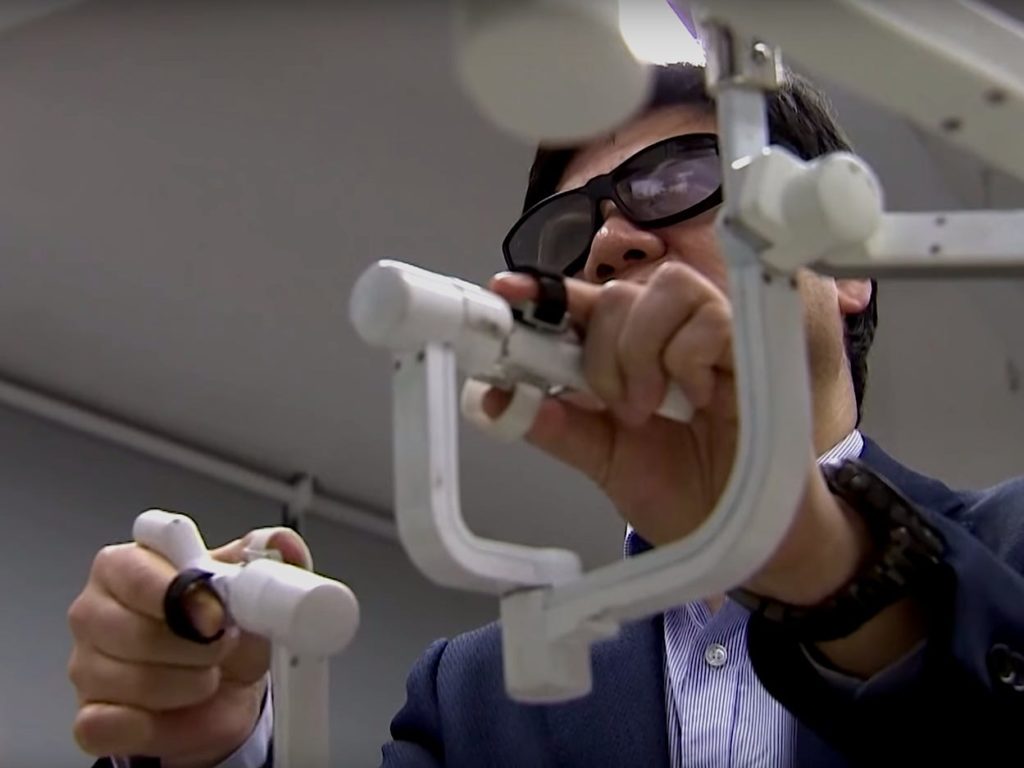
You may wonder what sets 5G apart from its predecessors. To the layman, it is quite simple as 5G brings a larger than ever before network capacity, more availability of network resources, and near-seamless user experience. It allows for safer transportation, remote healthcare, and logistic tracking, thus, facilitating a myriad of industries in countless ways. An example of how 5G will revolutionize healthcare is the Remote 5G Surgery that has been initiated in China earlier this year. A doctor in Sanya used 5G to perform brain surgery on a Parkinson’s patient in Beijing from 1,900 miles away in real-time. The most recent predecessor of 5G offers super-fast speeds but still leaves room for lags up to 2 seconds which could prove fatal in a situation like this but 5G made it a whopping success with lag-time just around 2 milliseconds between devices.
The average user will be able to consume up to 11 GB of data per month by 2022 as compared to the current 2 GB. With the COVID and post-COVID global trajectory of digital communication and the exponential growth of video material, 5G will massively increase the user’s capability to consume data online. To put it into context, imagine being able to download a movie in 8K 500% faster than before.
To those interested in exploring the underlying technological features, however, the features are more extensive. 5G is based on Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) which is a way of controlling digital signals across various channels without leaving room for interference. This allows it to deliver an exponentially greater amount of flexibility and scalability allowing the user to access more on their end. 5G utilizes the 5G NR air interface and a wider bandwidth such as the 6GHz. It is built to operate in lower bands like sub-6 GHz and higher bands such as the 24 GHz and beyond.

5G offers better and faster bandwidth than its predecessor 4G LTE and also has the capability to offer services such as mission-critical communication and connection to the massive Internet of Things.
5G is set to have a greater impact on the global economy than its predecessors by potentially changing the game for many industries such as machinery, automobiles, etc. 5G does not only apply to smartphone users and can also impact your home internet service. ISPs will now be able to provide 5G infrastructure and knock fiber and cable solutions right out of the park.

As of right now, 5G is available in over 35 countries including Canada, Germany, Hong Kong, China, Bahrain, United States, and Saudi Arabia, and is slowly but surely coming to the rest of the world.
To be able to use 5G services, though, you will have to upgrade your cellphones to newer models that have the capacity to support this powerhouse network. Some phones that are 5G compatible and are available in the market right now include Xiaomi Redmi K20 Pro, Xiaomi Mi 9, Xiaomi Mi 10 Pro, Oppo Reno 5G, Google Pixel 5G, Samsung Galaxy S20 5G, Samsung Galaxy Z Flip, and Samsung Galaxy Note20 Ultra 5G. As of now, though, none of Apple’s iPhone variants have the capability to support 5G and will need a hardware re-design to facilitate it in the future.









Leave a Reply